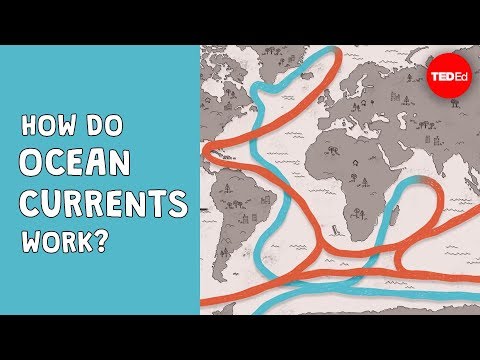
Winds, water density, and tides all drive ocean currents. Coastal and sea floor features influence their location, direction, and speed. Earth’s rotation results in the Coriolis effect which also influences ocean currents.
Q. What are deep ocean currents driven by?
However, ocean currents also flow thousands of meters below the surface. These deep-ocean currents are driven by differences in the water’s density, which is controlled by temperature (thermo) and salinity (haline). This process is known as thermohaline circulation.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are deep ocean currents driven by?
- Q. What are characteristics of deep ocean currents?
- Q. What has a major role regulating global temperatures?
- Q. How do ships get out of the Black Sea?
- Q. Are US submarines in the Black Sea?
- Q. Is Crimea Russian or Ukrainian?
- Q. How do temperature and salinity affect deepwater currents?
- Q. How do temperature and salinity affect deepwater currents quizlet?
- Q. What are two major drivers of surface ocean current and deep ocean current?
- Q. What are the 5 major ocean currents?
- Q. What are the two types of currents?
- Q. What are the 3 types of currents?
- Q. How many different currents are there?
- Q. What are the different currents?
- Q. What are 3 types of ocean currents?
- Q. What is the fastest ocean current?
- Q. What are the major types of currents?
- Q. What is difference between wave and current?
- Q. Which ocean current determines weather changes?
- Q. Which ocean current is a warm current?
- Q. Which two currents are considered to be warm currents?
- Q. What is a deep current?
- Q. Which ocean current is responsible for the warm moist air what type of current is it?
- Q. Is the Kuroshio current warm or cold?
- Q. Is the Peru Current warm or cold?
- Q. Why is California current cold?
- Q. Is the California Current warm?
- Q. Are California beaches cold?
- Q. Is the California current strong or weak?
- Q. Is the California Current fast or slow?
- Q. Is the California current slow?
- Q. What does the California current impact?
- Q. Where does the California current flow?
- Q. Why is Atlantic Coast colder than Pacific?
- Q. Why is the West Coast so cold?
Q. What are characteristics of deep ocean currents?
Deep ocean currents are density-driven and differ from surface currents in scale, speed, and energy. Water density is affected by the temperature, salinity (saltiness), and depth of the water.
Q. What has a major role regulating global temperatures?
Water vapor and clouds are the major contributors to Earth’s greenhouse effect, but a new atmosphere-ocean climate modeling study shows that the planet’s temperature ultimately depends on the atmospheric level of carbon dioxide.
Q. How do ships get out of the Black Sea?
The Bosporus Strait connects it to the small Sea of Marmara which in turn is connected to the Aegean Sea via the Strait of the Dardanelles. To the north, the Black Sea is connected to the Sea of Azov by the Kerch Strait….
| Black Sea | |
|---|---|
| Type | Sea |
| Primary inflows | Danube, Dnieper, Don, Dniester, Kuban |
| Primary outflows | Bosporus |
Q. Are US submarines in the Black Sea?
The U.S. Navy routinely operates in the Black Sea consistent with international law, including the Montreux Convention. Ross is one of four U.S. Navy destroyers based in Rota, Spain, and assigned to Commander, Task Force 65 in support of NATO’s Integrated Air Missile Defense architecture.
Q. Is Crimea Russian or Ukrainian?
The Republic of Crimea is a federal subject (republic) of Russia located on the disputed Crimean Peninsula, which was annexed by Russia from Ukraine in 2014, but is still internationally recognized as being part of Ukraine.
Q. How do temperature and salinity affect deepwater currents?
As temperatures and salinity levels of water increase, the water rises to the surface where it creates currents as it moves to colder regions. They create density differences that cause dense deepwater currents to flow toward the equator where they displace less dense, warmer water above them.
Q. How do temperature and salinity affect deepwater currents quizlet?
Terms in this set (25) temperature and salinity changes at surface cause high-density water to form, which sinks. Dense water spreads beneath the surface, causing deep currents. These currents have vertical motion.
Q. What are two major drivers of surface ocean current and deep ocean current?
Two major kinds of currents define the planet’s oceans: surface currents driven by wind and deep-water currents driven by variations in seawater density.
Q. What are the 5 major ocean currents?
There are five major gyres: the North Atlantic, the South Atlantic, the North Pacific, the South Pacific and the Indian Ocean Gyre, see figure 1. The Antarctic Circumpolar Current is situated in the Southern Ocean and constantly circles around Antarctica because there are no land masses to interrupt the currents.
Q. What are the two types of currents?
There are two kinds of current electricity: direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC). With direct current, electrons move in one direction. Batteries produce direct current. In alternating current, electrons flow in both directions.
Q. What are the 3 types of currents?
Currents, The North Equatorial Current, the Gulf Stream, the North Atlantic Current, and the Canary Current.
Q. How many different currents are there?
There are two types of currents, surface currents and deep water currents, that dictate how and where water will move. Scientists study currents to learn more about how the ocean works mechanically, as well as using the speed and location of currents as a way to measure changes in large bodies of water.
Q. What are the different currents?
There are many types of currents such as those driven by salinity, wind, temperature or the Coriolis effect. Two of the most commonly identified are surface currents and deep ocean currents. Surface currents are driven by winds, are fast and make up 10% of the world’s oceans.
Q. What are 3 types of ocean currents?
There are many types of currents such as those driven by salinity, wind, temperature or the Coriolis effect. Two of the most commonly identified are surface currents and deep ocean currents.
Q. What is the fastest ocean current?
The Gulf Stream
Q. What are the major types of currents?
The two basic types of currents – surface and deep-water currents – help define the character and flow of ocean waters across the planet.
Q. What is difference between wave and current?
Waves are created by the wind and then radiate in all directions away from the disturbance. Currents represent the movement of water particles which is controlled by winds and density differences. Waves and currents can travel in opposite directions.
Q. Which ocean current determines weather changes?
Answer: The Gulf Stream determines climate change. Thermohaline circulation occurs due to the difference in the temperatures, densities, and salinities of the waters, and determines climate changes.
Q. Which ocean current is a warm current?
List of Ocean Currents of the World
| Name of Current | Nature of Current |
|---|---|
| North Equatorial Current | Hot or Warm |
| Kuroshio Current | Warm |
| North Pacific Current | Warm |
| Alaskan Current | Warm |
Q. Which two currents are considered to be warm currents?
b) Major currents of the North Atlantic Ocean are: Gulf Stream (warm), North Atlantic Drift (warm) and Canary Current (cold). c) Major currents of South Atlantic Ocean are: Benguela Current (cold) and Brazil Current (warm).
Q. What is a deep current?
The ocean currents known since antiquity are called surface currents. The majority of the ocean’s currents take the form of a temperature- and salinity-driven “conveyor belt” that slowly churns water within the abyssal depths. These loops of water circulation are called deep currents.
Q. Which ocean current is responsible for the warm moist air what type of current is it?
Gulf Stream
Q. Is the Kuroshio current warm or cold?
The surface waters of the Kuroshio Current are warm and salty. This is because the Kuroshio starts in the tropics where the westward flowing North Equatorial Current reaches the western boundary of the North Pacific.
Q. Is the Peru Current warm or cold?
As it is a cold current, except at times of the phenomenon known as El Niño (q.v.), the Peru Current brings fog to the nearby coast but also helps to keep the coast one of the most intensely arid areas in the world.
Q. Why is California current cold?
The water along the coast of California is cold for a couple of reasons. First, the California Current brings cold water from Alaska southward along the coast. And second, cold water from the deep ocean comes up to the surface through a process called upwelling. The water from the deep ocean is full of nutrients.
Q. Is the California Current warm?
The California Current is a cold water Pacific Ocean current that moves southward along the western coast of North America, beginning off southern British Columbia and ending off southern Baja California Sur.
Q. Are California beaches cold?
The ocean off of California is actually quite cold, because of the California Current carrying cold water from British Columbia south to southern California. Summertime sea surface temperature is appreciably warmer (maybe a few degrees Celsius), though the water still certainly feels cold.
Q. Is the California current strong or weak?
The California Current is what scientists call an eastern boundary current. Strong current systems flow along the east side (or boundary) of all of Earth’s major ocean basins. They tend to move water toward the equator, and they are prone to strong upwelling.
Q. Is the California Current fast or slow?
Question: Can you tell us what the speeds are that correspond to the California Current ? Schwartzlose: The average speed of the general California Current is about 4 to 4 knot (12.5-25 cm/sec) .
Q. Is the California current slow?
The California Current’s surface velocity is commonly less than 10 in. (25 cm) per second, transporting about cu ft (cu m) of water per second above 3,300 ft (1,000 m). The temperature and salinity of its waters vary with seasonal variations in upwelling, insolation, and flow.
Q. What does the California current impact?
The California Current moves less water than the Gulf Stream does. But the California Current has a big effect on the climate of the West Coast of the United States. Usually, the climate along the West Coast is cooler than the climate of inland areas at the same latitude and elevation.
Q. Where does the California current flow?
The California current is the eastern boundary current of the North Pacific Gyre, running southward from British Columbia, Canada to Baja California, Mexico. This current draws cool, nutrient rich waters from the Alaska current down along the western coast of North America.
Q. Why is Atlantic Coast colder than Pacific?
That is true because ocean waters rotate in clockwise fashion. This means Atlantic waters travel to the U.S. East Coast from the south and are relatively warm compared with West Coast Pacific waters that arrive from the north out of the chilly Gulf of Alaska.
Q. Why is the West Coast so cold?
The ocean currents on the West coast flow North to South. The Pacific is very deep just off shore. The wind blows over this cooler water, making you feel cooler. The wind blows over this warmer water and feels much warmer.