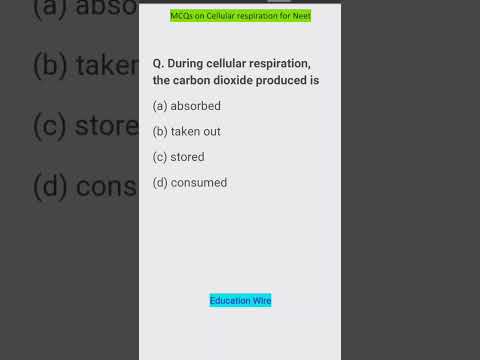
During the process of cellular respiration, carbon dioxide is given off as a waste product. This carbon dioxide can be used by photosynthesizing cells to form new carbohydrates. Also in the process of cellular respiration, oxygen gas is required to serve as an acceptor of electrons.
Q. What is the cycle of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the cycle of cellular respiration?
- Q. Why is photosynthesis and cellular respiration a cycle?
- Q. Where do the steps of cellular respiration occur?
- Q. Where does cellular respiration release co2?
- Q. What produces CO2 in cellular respiration?
- Q. What are the two reactants in the cellular respiration equation?
- Q. Why is cellular respiration considered an efficient process?
- Q. What is the most efficient process in cellular respiration?
- Q. Why is cellular respiration considered catabolic?
- Q. What is different about cellular respiration when compared to photosynthesis?
- Q. Are photosynthesis and cellular respiration catabolic or anabolic reactions?
- Q. What type of cells goes through the process of aerobic cellular respiration?
- Q. Is cellular respiration an anabolic reaction?
- Q. What type of reaction is cellular respiration Endergonic or Exergonic?
- Q. What is an example of an anabolic reaction?
Q. Why is photosynthesis and cellular respiration a cycle?
Cellular respiration and photosynthesis are important parts of the carbon cycle. The carbon cycle is the pathways through which carbon is recycled in the biosphere. While cellular respiration releases carbon dioxide into the environment, photosynthesis pulls carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere.
Q. Where do the steps of cellular respiration occur?
The process begins in the cytoplasm and is completed in a mitochondrion. Cellular respiration occurs in three stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and electron transport. Glycolysis is an anaerobic process. The other two stages are aerobic processes.
Q. Where does cellular respiration release co2?
mitochondria
Q. What produces CO2 in cellular respiration?
During aerobic cellular respiration, glucose reacts with oxygen, forming ATP that can be used by the cell. Carbon dioxide and water are created as byproducts. Water and carbon dioxide are released as byproducts.
Q. What are the two reactants in the cellular respiration equation?
The Reactants Oxygen and glucose are both reactants of cellular respiration.
Q. Why is cellular respiration considered an efficient process?
Why is cellular respiration considered to be much more efficient than glycolysis alone? Cellular respiration enables the cell to produce 34 more ATP molecules per glucose molecule in addition to the 2 ATP molecules obtained from glycolysis.
Q. What is the most efficient process in cellular respiration?
Aerobic cell respiration (glycolysis + the Krebs cycle + respiratory electron transport) produces 36 ATP/glucose consumed. Aerobic cell respiration is roughly 18 times more efficient than anaerobic cell respiration. Your cells require a lot of energy and are dependent on the high efficiency of aerobic respiration.
Q. Why is cellular respiration considered catabolic?
Catabolism: Cellular respiration Cellular respiration is a catabolic process during which glucose is broken down to release usable energy for a cell. As in all catabolic processes, cellular respiration releases energy which can then be harnessed and used by other reactions in the cell.
Q. What is different about cellular respiration when compared to photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis makes the glucose that is used in cellular respiration to make ATP. While photosynthesis requires carbon dioxide and releases oxygen, cellular respiration requires oxygen and releases carbon dioxide. It is the released oxygen that is used by us and most other organisms for cellular respiration.
Q. Are photosynthesis and cellular respiration catabolic or anabolic reactions?
Photosynthesis, which builds sugars out of smaller molecules, is a “building up,” or anabolic, pathway. In contrast, cellular respiration breaks sugar down into smaller molecules and is a “breaking down,” or catabolic, pathway.
Q. What type of cells goes through the process of aerobic cellular respiration?
Aerobic respiration is characteristic of eukaryotic cells when they have sufficient oxygen and most of it takes place in the mitochondria.
Q. Is cellular respiration an anabolic reaction?
Catabolic process is the process, which break down large molecule into smaller units, that are either oxidized to release energy or used in other metabolic reaction. Anabolic Process is the process that construct large molecules from smaller units. So, Respiration is a catabolic process.
Q. What type of reaction is cellular respiration Endergonic or Exergonic?
Photosynthesis is an endergonic (energy-consuming) process. Cellular respiration is an exergonic (energy-releasing) process.
Q. What is an example of an anabolic reaction?
An example of an anabolic reaction is the synthesis of glycogen from glucose. An example of a catabolic reaction is the process of food digestion, where different enzymes break down food particles so they can be absorbed by the small intestine.