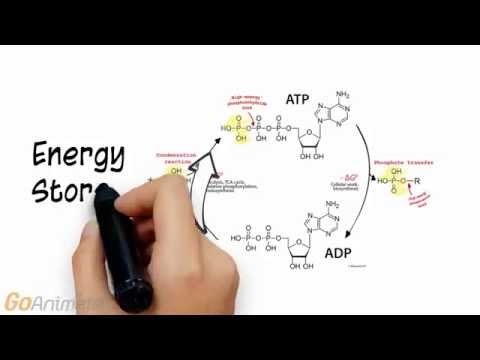
To sustain muscle contraction, ATP needs to be regenerated at a rate complementary to ATP demand. Three energy systems function to replenish ATP in muscle: (1) Phosphagen, (2) Glycolytic, and (3) Mitochondrial Respiration.
Q. What does ATP produce when broken down?
The by-products of the breakdown of ATP are adenosine diphosphate (ADP), which is the remaining adenosine and two (di) phosphate groups, and one single phosphate (Pi) that is ‘on its own’.
Table of Contents
- Q. What does ATP produce when broken down?
- Q. How can I increase ATP naturally?
- Q. Can you take ATP supplements?
- Q. Can adenosine be given orally?
- Q. Does adenosine stop your heart?
- Q. What is another name for adenosine?
- Q. How safe is Adenosine?
- Q. What does adenosine do to the body?
- Q. What drug class is Adenosine?
- Q. How long does adenosine stay in your system?
- Q. When should you not take adenosine?
- Q. What does Adenosine Injection feel like?
- Q. Does adenosine affect blood pressure?
- Q. What is adenosine used to treat?
- Q. What is adenosine heart rate?
- Q. Why is adenosine important?
- Q. What causes adenosine release?
- Q. Is adenosine a hormone?
- Q. What causes too much adenosine?
Q. How can I increase ATP naturally?
Boost your ATP with fatty acids and protein from lean meats like chicken and turkey, fatty fish like salmon and tuna, and nuts. While eating large amounts can feed your body more material for ATP, it also increases your risk for weight gain, which can lower energy levels.
Q. Can you take ATP supplements?
ATP is the primary source of energy for the cells, and supplementation may enhance the ability to maintain high ATP turnover during high-intensity exercise. Oral ATP supplements have beneficial effects in some but not all studies examining physical performance.
Q. Can adenosine be given orally?
Oral ATP administration can increase post-exercise blood flow, and may be particularly effective during exercise recovery.
Q. Does adenosine stop your heart?
— This biochemical will stop your heart — just long enough to be useful. In the ED, adenosine is used to terminate supraventricular tachycardias (SVTs). It is also used by cardiologists for pharmacologic stress testing.
Q. What is another name for adenosine?
Adenosine is available under the following different brand names: Adenocard, and Adenoscan.
Q. How safe is Adenosine?
Abstract. Adenosine is an effective, safe drug for the diagnosis and treatment of paroxysmal tachycardias in adult and pediatric patients. A starting dose of 0.05-0.10 mg/kg as a rapid bolus injection is recommended for infants and children. An electrophysiologic effect can be expected within 20 seconds after injection …
Q. What does adenosine do to the body?
In the brain adenosine is an inhibitory neurotransmitter. This means, adenosine can act as a central nervous system depressant. In normal conditions, it promotes sleep and suppresses arousal. When awake the levels of adenosine in the brain rise each hour.
Q. What drug class is Adenosine?
Nucleoside
Q. How long does adenosine stay in your system?
The half-life of Adenocard (adenosine injection) is less than 10 seconds. Thus, adverse effects are generally rapidly self-limiting. Treatment of any prolonged adverse effects should be Page 6 individualized and be directed toward the specific effect.
Q. When should you not take adenosine?
Patients with irregular heart rates, especially atrial fibrillation, patients with PSVT mimics such as atrial flutter with 2:1 conduction or sinus tachycardia in a dehydrated or stressed patient should never receive adenosine. Adenosine should never be used in wide irregular tachycardias.
Q. What does Adenosine Injection feel like?
Some people describe it as chest pain. Others say is feels like they are going to die.
Q. Does adenosine affect blood pressure?
Adenosine lowers blood pressure (top), heart rate (middle), and renal sympathetic nerve activity (RSNA) (bot- tom) in this model These effects are similar to those obtained with excitatory amino acid glutamate.
Q. What is adenosine used to treat?
Likely Effective for A heart condition marked by episodes of rapid heart rate (paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia). Adenosine is used as a prescription-only intravenous medicine to treat certain kinds of irregular heartbeat.
Q. What is adenosine heart rate?
In terms of its electrical effects in the heart, adenosine decreases heart rate and reduces conduction velocity, especially at the AV node, which can produce atrioventricular block.
Q. Why is adenosine important?
Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics Adenosine is a naturally occurring nucleoside which is present in various forms in all cells of the body. It is an essential component of the energy production and utilization systems of the body.
Q. What causes adenosine release?
Prolonged increased neural activity in the brain’s arousal centers triggers the release of adenosine, which in turn slows down neural activity in the arousal center areas.
Q. Is adenosine a hormone?
Adenosine is an endogenous agonist of the ghrelin/growth hormone secretagogue receptor. However, while it is able to increase appetite, unlike other agonists of this receptor, adenosine is unable to induce the secretion of growth hormone and increase its plasma levels.
Q. What causes too much adenosine?
The accumulation of adenosine in the body is related to the quantity of caffeine consumed during the day. By drinking beverages with high levels of caffeine, the body builds up an excessive amount of adenosine.