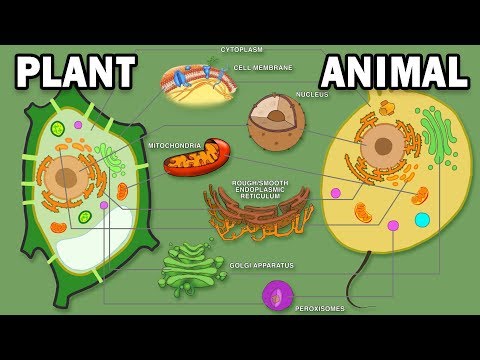
The lysosomes are the animal cell’s “garbage disposal”, while in plant cells the same function takes place in vacuoles. The central vacuole plays a key role in regulating a plant cell’s concentration of water in changing environmental conditions.
Q. What are the similarities between a lysosome and a vacuole?
What are the Similarities Between Lysosome and Vacuole? Both lysosome and vacuole are cell organelles. Both are surrounded by a membrane. Both are present in eukaryotic cells.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the similarities between a lysosome and a vacuole?
- Q. What structures do plant cells have that animal cells do not have?
- Q. Why do plant cells have walls that animal cells do not have?
- Q. Do animal cells have a vacuole?
- Q. Why do animals not need vacuoles?
- Q. Do humans have cell membranes?
- Q. What would happen if plant cells had no cell walls?
- Q. What would happen if a cell didn’t have enough channels?
- Q. What would be like if cells never exist?
- Q. What would life be like without cells?
- Q. Can life exist without a cell?
- Q. Why is it important to know about cells?
- Q. What are some interesting facts about cells?
- Q. Why did HeLa cells not die?
- Q. Are HeLa cells still alive?
- Q. Are all cancer cells immortal?
Q. What structures do plant cells have that animal cells do not have?
Major structural differences between a plant and an animal cell include:
- Plant cells have a cell wall, but animals cells do not.
- Plant cells have chloroplasts, but animal cells do not.
- Plant cells usually have one or more large vacuole(s), while animal cells have smaller vacuoles, if any are present.
Q. Why do plant cells have walls that animal cells do not have?
Plant cell needs cell wall whereas animal cell do not because the plants need rigid structure so that they can grow up and out . All cells have cell membranes, and the membranes are flexible. So animal cells can have various shapes, but plant cells only have the shapes of their cell walls.
Q. Do animal cells have a vacuole?
Vacuole. A vacuole is a membrane-bound cell organelle. In animal cells, vacuoles are generally small and help sequester waste products. In plant cells, vacuoles help maintain water balance.
Q. Why do animals not need vacuoles?
Animal cells have small vacuoles because they don’t need to store as much water as other organisms such as plants.
Q. Do humans have cell membranes?
Human cells only have a cell membrane. The cell wall is primarily made of cellulose, which is composed of glucose monomers. As the outermost layer of the cell, it has many important functions. It prevents the plasma membrane from bursting as a result of water uptake and it determines the overall cell shape and texture.
Q. What would happen if plant cells had no cell walls?
If cell wall is absent in plant cell then all the functioning of all the cell organelles present inside the cell would be affected as diffusion of various substances would not occur. Due to absence of turgor pressure, the cell will not bear the concentration of solution (either hypertonic or hypotonic) and will burst.
Q. What would happen if a cell didn’t have enough channels?
Consequence for a cell, if the cell membrane is not large enough to have adequate channels? Cannot bring in nutrients and remove waste. Cells wouldn’t be able to carry out all the functions.
Q. What would be like if cells never exist?
Cells make up tissues, like connective tissue, skeletal tissue, nervous tissue and fatty tissue. With no cells, there are no tissues or organs. Humans would not exist.
Q. What would life be like without cells?
And while some cells can live on their own, others need to be part of a larger group of cells to survive. The only example of something “alive” without cells might be viruses (like what causes chicken pox or the flu) which are just packets of protein and DNA.
Q. Can life exist without a cell?
Non-cellular life, or acellular life is life that exists without a cellular structure for at least part of its life cycle. The primary candidates for non-cellular life are viruses. Some biologists consider viruses to be living organisms, but others do not.
Q. Why is it important to know about cells?
Cells provide structure and function for all living things, from microorganisms to humans. Scientists consider them the smallest form of life. Cells house the biological machinery that makes the proteins, chemicals, and signals responsible for everything that happens inside our bodies.
Q. What are some interesting facts about cells?
Cells are the basic building blocks of living things. The human body is composed of trillions of cells, all with their own specialised function. Cells are the basic structures of all living organisms. Cells provide structure for the body, take in nutrients from food and carry out important functions.
Q. Why did HeLa cells not die?
Like many other cancer cells, HeLa cells have an active version of telomerase during cell division, which copies telomeres over and over again. This prevents the incremental shortening of telomeres that is implicated in aging and eventual cell death.
Q. Are HeLa cells still alive?
The HeLa cell line still lives today and is serving as a tool to uncover crucial information about the novel coronavirus. HeLa cells were the first human cells to survive and thrive outside the body in a test tube.
Q. Are all cancer cells immortal?
Almost all cancer cells are immortal, having overcome cellular senescence by reactivating or upregulating telomerase, a cellular reverse transcriptase that stabilizes telomeres.